The National Property Summit 2022

Join Neil Bannon at the upcoming National Property Summit 2022 on 1st December discussing the latest challenges and opportunities facing Irish commercial property with this expert panel.

Join Neil Bannon at the upcoming National Property Summit 2022 on 1st December discussing the latest challenges and opportunities facing Irish commercial property with this expert panel.
 Whatever the short balance of the year has in store, there is little doubt that in 2022 a rubicon was crossed for assets that are not scoring well with their ESG credentials. The RICS made sure valuers took the step to acknowledge the importance of ESG credentials on buildings and their impact on values with the publication of a new guidance note effective from January this year. Also in 2022, more than ever, both occupiers and owners made known their absolute preference for ESG compliant buildings. In the office sector in Q3 over 85% of city take-up related to ESG compliant offices.
Whatever the short balance of the year has in store, there is little doubt that in 2022 a rubicon was crossed for assets that are not scoring well with their ESG credentials. The RICS made sure valuers took the step to acknowledge the importance of ESG credentials on buildings and their impact on values with the publication of a new guidance note effective from January this year. Also in 2022, more than ever, both occupiers and owners made known their absolute preference for ESG compliant buildings. In the office sector in Q3 over 85% of city take-up related to ESG compliant offices.
The Bannon Professional Services team has embraced the RICS Valuation Practice Guidance Note titled ‘Sustainability and ESG in Commercial Property Valuation and Strategic Advice’ in undertaking our valuations. In doing so we demonstrate how we have considered sustainability and ESG credentials in our valuation approach, calculations and commentary.
Our experience in 2022 is that the majority of owners have come to realise the importance of ESG credentials in terms of how they influence value. For some owners, mainly outside of the more professional participants, there is still the ‘unknown’ in terms of the actual cost to rectify their asset where there is a deficiency. In relation to older assets where there is a shortfall in data it has been necessary for us to ask for specialist third party inputs, primarily in relation to the cost of bringing the asset up to an acceptable ESG standard. On some of those occasions we have been challenged with the findings as, often is the case, the cost of the upgrade is not supported by a corresponding uplift in value. This is more typical where the asset is in a secondary location. In those circumstances we have then also looked at alternative uses or otherwise materially adjusted the carrying value.
All said, valuing properties which have a shortfall in terms of being a credible ESG asset requires an in-depth understanding of a myriad of factors. They include market variables, competition from compliant buildings, and costs.
We have learned a lot in the past 24 months, but with much more to learn as the focus on ESG continues with pace. The benchmark that buildings must reach in terms of a new rating post being redeveloped is still unclear. Also, whilst valuers will request a lot from owners as part of their due diligence, in many cases definitive answers are not yet available. What we do now know is that the value gap will continue to widen between those that do offer enhanced ESG credentials and those that don’t.
Author: Paul Doyle, Managing Director, Bannon
Date: 10th November 2022

A cursory look at both the third quarter and year-to-date property investment volume data would indicate that it’s a case of “steady as she goes” in the market but as always, the proverbial devil is in the detail. When you pull back the curtain on the statistics, the current institutional investment mantra of “beds, sheds and meds” is reflected in the true underlying trends.
:quality(70)/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/irishtimes/RD72OWG6Z5BTFCE3SO7DUQKALI.jpg)
At first glance, investment volumes for the third quarter show that offices hold the lead at 37.7 per cent closely followed by residential at 36 per cent. Year to date shows an even stronger position for offices at 43.5 per cent and residential at 29.9 per cent. However, two key transactions shroud a huge shift in the market and highlight the importance of both the residential sector and the movement in non-office investments.
If we exclude the €1.089 billion Hibernia Reit (Hibernia Real Estate Group) transaction from the second quarter (which arguably should not have been included as it was a corporate acquisition) and the one-off €500 million Salesforce headquarter deal from the third quarter, the lay of the land changes dramatically. The result is that the residential sector exceeds 50 per cent of third-quarter volumes and 44.4 per cent of the year-to-date volumes. Conversely, the office sector falls to a mere 17.7 per cent of the quarter and 17.6 per cent for the year-to-date.
This is a dramatic transition for the offices sector, which accounted for 39 per cent of market transactions in 2020 and 28 per cent in 2021. A number of factors are likely contributing to this shift. Among them is the depleting availability of developer-led schemes for trade, concern attaching to the occupational impact of the working-from-home (WFH) phenomenon, and the unknown impact of required ESG retrofitting to standing stock.
As a consequence of the decline in the office sector’s relative importance we are seeing a number of alternative sectors come to the fore. The industrial sector has seen the reverse trend as the desire for sheds from institutions is unabated and the supply side is relatively elastic. It has grown from a mere 4 per cent in 2019 and 8.8 per cent in 2020 to 13.1 per cent currently, almost on a par with office. Similarly, the healthcare sector, from near obscurity, comes to represent almost 8 per cent of investment volumes.
When you add all this up, excluding the Hibernia and Salesforce deals, “beds, sheds and meds” made up over 65 per cent of investment-transaction volume in the year to date. When you consider that sheds and medss collectively amounted to mere rounding errors in the investment statistics 10 years ago, it demonstrates just how much the real-estate landscape has shifted and reinforces the sheer naivety of assuming that the market today is a clear indicator of future trends
The increased availability of so-called “grey space” and sublet opportunities, eg LinkedIn in Wilton Place, may further reduce speculative office development and consequent supply. The roll-out of primary healthcare centres across the country will support continued growth in investment the healthcare sector. These trends point to the future of the investment market and are the current focus of our research and consultancy team.

Occupancy rates continue to improve and retail sales reach an inflection point.
To view the full report, please click here.
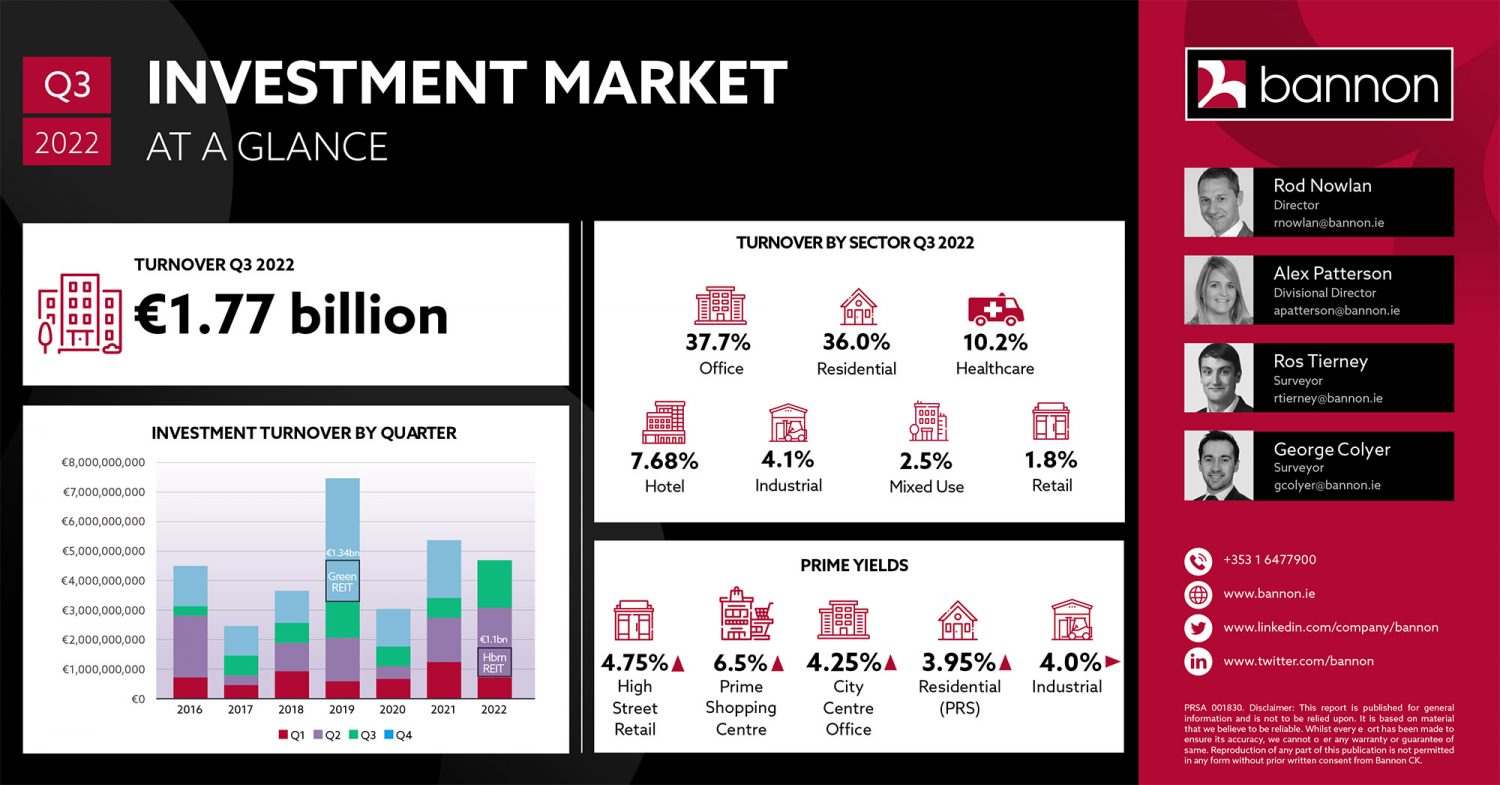
The Irish Commercial Real Estate (CRE) sector performed strongly in Quarter 3 with over €1.77 billion invested in Irish commercial property across 47 transactions. This figure was underpinned by the Ronan Group’s sale of the Salesforce HQ on Spencer Place and a 204-bedroom hotel for €500 million, the largest transaction by some margin. Annual turnover will significantly exceed €5bn for 2022 and establish the second strongest year on record after 2019.
To view the full report, click here.
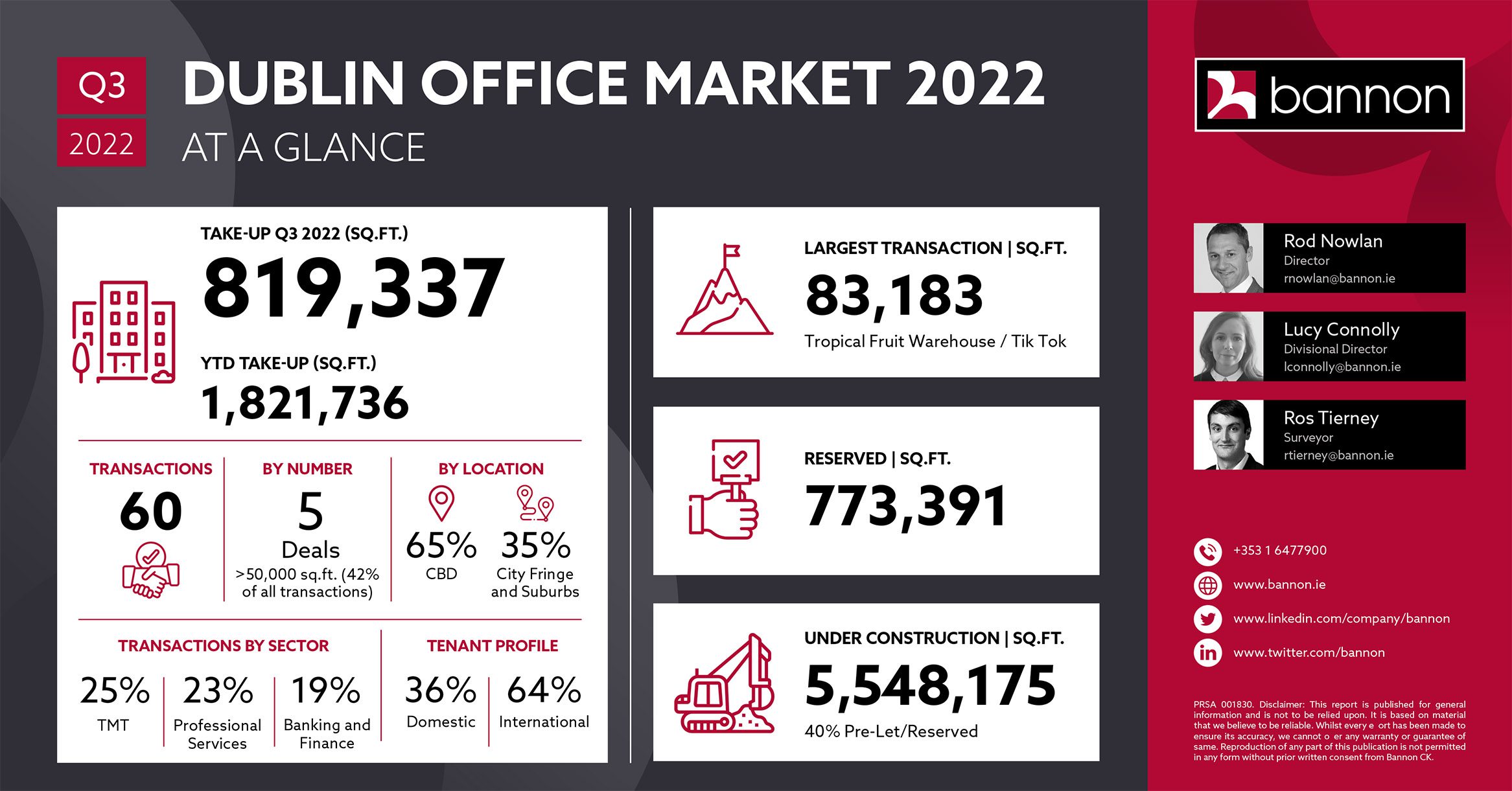
The Dublin office market performed strongly in Q3 with take up reaching 819,337 sq.ft. across 60 transactions, bringing the year-to-date figure to just over 1,820,000 sq.ft. To put this figure in context, it represents a 77% increase on Q3 2021, a 256% increase on Q3 2020 and 134% increase on Q3 2019 levels (pre covid).
As we move forward into the final quarter, there is over 770,000 sq.ft. of office accommodation reserved and active requirements of c. 3 million sq.ft. which bodes well for the remainder of the year.

Following an extended period of “head burying”, most property fund managers are bracing themselves for material negative valuer adjustments across their portfolios (with the potential exception of retail which has already been massively discounted). This trepidation is clearly derived from the escalating impacts of the war in Ukraine, spiralling inflation, rising interest rates, looming recession in both the US and across the EU, and now the calamitous UK economic situation. However, there is one area of the property market where the impact of these issues will be magnified and, to add to its woes, systemic shortfalls exposed which have been historically overlooked. This is the area of non-ESG (environmental, social and governance) compliant offices, many of which are already on their way to becoming “stranded assets”.
If a building does not meet ESG requirements and the cost of improving it to satisfy these exceeds the required market return, the building in question can be considered a stranded asset. In the valuers’ defence, the office occupational market has been very slow in adjusting to the environmental agenda
Until relatively recently very few valuers were appropriately differentiating between offices that could satisfy occupier ESG requirements and those that could not. This is especially the case for those perceived “modern schemes” constructed in the past 10 years but whose energy conservation specification does not satisfy the 2017 Part L building guidelines — the effective start of the nZEB (nearly zero energy building) standards. Even if ESG upgrades were accounted for, the costs being applied were often only a fraction of the reality. These costs, which include the likes of glass/facade replacement, plant enhancement/replacement, electrical hardware upgrades, new BMS (building management systems), PV (photovoltaic) installation, rainwater harvesting and general water conservation initiatives are now materially higher and rising.
A scarcity of materials and competition for labour and expertise is unlikely to see these costs abate in the next few years as the scale of the issue becomes apparent. The Bannon office team estimates than less than 15 per cent of Dublin’s current office stock is actually ESG compliant.
In the valuers’ defence, the office occupational market has been very slow in adjusting to the environmental agenda, and rent is ultimately the primary driver of value. However, since the ramifications of the EU’s sustainable finance directive (adopted in April 2021) and the UK’s escalating Minimum Energy Efficiency Standards (MEES) have become clearer, and with various recent high-profile climate events driving public (and corporate) opinion, a sea change in attitudes has swept over the occupational market.
If we look back at this quarter’s office lettings, the transition in the market’s thinking is clear. There was almost 400,000sq ft of take-up in Dublin’s core central business district (Dublin 1, 2 and 4) with 86 per cent of this accounted for by ESG-compliant space. Clearly there is now a firmly established two-tier office occupational market in the city centre, namely ESG-compliant offices and the rest. Interestingly, from a further review of this quarter’s take-up, it is clear that ESG is still not a priority in the more “value-focused” suburban locations with a mere 15 per cent of the 275,000sq ft of take-up outside of Dublin 1,2 and 4 being ESG-compliant. However, the pressure on all occupiers is likely to intensify further in January 2023 when the rest of the taxonomy regulations — technical screening criteria (TSC) and regulatory technical standards (RTS) — and the second phases of financial services sector regulation and the FCA climate-related disclosure regime come into effect.
This will be particularly difficult for suburban assets to react to as the rent available in these locations is unlikely to be sufficient to support ESG retrofits.
The extent of this micro-sector’s woes doesn’t stop there either. The “latent carbon” movement is also upon us meaning that it will become increasingly difficult to knock down existing buildings. Increased density and height can support the economics of ESG which is often maximised by demolition. The increasing focus on preserving latent carbon will mean the best that will be on offer for these buildings is to be extended vertically and horizontally, which will have both structural and planning limitations. As a consequence, valuers are finally consulting their quantity-surveyor colleagues to determine the true scale of the issue. The “tic-tic” of the rollercoaster looks to be falling silent for this part of the market, and I’m not sure the current non-ESG compliant office owners will enjoy the ride to come.
There will however be a huge opportunity for those with the skills to efficiently transition these buildings back towards the institutional mainstream. In this regard, valuing and selling these assets will require an in-depth analysis of the true costs associated with bringing them up to standard. For some, the maths just will not work, while for others pursuing an alternate use may be the only avenue open to them.
 The Croí Cónaithe scheme, which has had €450m earmarked for it over the next three years, is designed for the State to plug the gap between the cost of construction and the market value of apartments. It relates to certain areas where the sales price achievable is less than the costs of development.
The Croí Cónaithe scheme, which has had €450m earmarked for it over the next three years, is designed for the State to plug the gap between the cost of construction and the market value of apartments. It relates to certain areas where the sales price achievable is less than the costs of development.
Funding will be provided solely for build-to-sell developments with apartments to be sold to individual owner-occupiers rather than build-to-rent schemes. It is hoped that the initiative will kick-start apartment developments in unviable locations particularly for first-time buyers, single people etc.
A report titled ‘The Real Costs of New Apartment Delivery’ by the Society of Chartered Surveyors in January 2021 found that a typical urban apartment block of between five to eight storeys, could cost between €380,000 and €451,000 to build. The variance should largely consist of site value depending on location. Build costs at these levels are generally above the sales prices achievable for most locations throughout Ireland outside of prime Dublin residential addresses. These construction costs will have also risen significantly in the intervening period.
Such a scheme which would invariably increase supply and the mix of new residential units being supplied to the market should be welcomed by all stakeholders. However, the perception that developers will somehow benefit from the public purse will be a key criticism to counteract. An open book analysis of input costs for each participating scheme and a cap on developers’ profit may be one way to ensure a satisfactory outcome for the return on investment by the State.
Niall Brereton BSc MRCIS MSCI is a Registered Valuer and Director of Professional Services at Bannon

We asked our leading experts for their views on achieving a sustainable future for the Irish commercial real estate sector:
General Commentary from Executive Chairman Neil Bannon
 Sustainability impacts everybody, whether it is investors securing the long-term value of their assets, corporate occupiers demonstrating their environmental credentials to clients and staff, retailers reacting to shifts in consumer demand or funding institutions protecting the security of their loan books. There is no part of the property market that is and will not be increasingly impacted by the move to a zero-carbon future. This realisation was the reason Bannon established EVIA 3 years ago; a consultancy business whose sole focus is the delivery of sustainable solutions to stakeholders in the commercial real estate sector. Since its inception EVIA, working hand in hand with the Bannon Management, Investment and Consultancy teams, has delivered dozens of sustainability projects including LED lighting projects, smart metres and energy monitoring, solar power installation and increasingly we are seeing demand from clients to provide an overarching strategy to put their entire relationship with real estate on a long-term sustainable footing.
Sustainability impacts everybody, whether it is investors securing the long-term value of their assets, corporate occupiers demonstrating their environmental credentials to clients and staff, retailers reacting to shifts in consumer demand or funding institutions protecting the security of their loan books. There is no part of the property market that is and will not be increasingly impacted by the move to a zero-carbon future. This realisation was the reason Bannon established EVIA 3 years ago; a consultancy business whose sole focus is the delivery of sustainable solutions to stakeholders in the commercial real estate sector. Since its inception EVIA, working hand in hand with the Bannon Management, Investment and Consultancy teams, has delivered dozens of sustainability projects including LED lighting projects, smart metres and energy monitoring, solar power installation and increasingly we are seeing demand from clients to provide an overarching strategy to put their entire relationship with real estate on a long-term sustainable footing.
The route to sustainability is both challenging and exciting. It can be costly and yet the alternative is much more expensive for stakeholders in the industry. By pursuing a sustainable strategy that coordinates zero-carbon delivery with valuation and asset management expertise, the journey can be efficient and ultimately profitable.
Retail from Directors James Quinlan and Darren Peavoy

 Institutional owners have very much embraced the ESG agenda, retailers have been slower to embrace from a property occupancy perspective, but this is changing. There is a trend in Institutional owners delivering ESG improvements via refurbishment works in advance of new lettings in prime high street locations. We are now seeing this being followed by some of the major international brands that are taking leases on these properties where they are committing to BREEAM GOOD (and higher) fitouts. Retailers have been proactive in retrofitting energy efficient initiatives including new LED lighting to reduce energy usage and benefit from reduced air conditioning requirements due to the reduced heat generation.
Institutional owners have very much embraced the ESG agenda, retailers have been slower to embrace from a property occupancy perspective, but this is changing. There is a trend in Institutional owners delivering ESG improvements via refurbishment works in advance of new lettings in prime high street locations. We are now seeing this being followed by some of the major international brands that are taking leases on these properties where they are committing to BREEAM GOOD (and higher) fitouts. Retailers have been proactive in retrofitting energy efficient initiatives including new LED lighting to reduce energy usage and benefit from reduced air conditioning requirements due to the reduced heat generation.
Valuations from Managing Director Paul Doyle and Director Niall Brereton

 The Bannon Professional Services team actively embraces and adheres to the latest RICS Valuation Practice Guidance Note titled ‘Sustainability and ESG in Commercial Property Valuation and Strategic Advice’ when undertaking valuation instructions. This Guidance Note requires the valuer to demonstrate how they have considered sustainability and ESG credentials in their valuation approach, calculations and commentary. It may be necessary, depending on the nature of the instruction, for the valuer to seek specialist investigations by a third party advising as to the ability and estimated cost to bring an asset up to modern standards. Valuing assets of this nature requires an in-depth analysis of the true costs associated with bringing them up to standard.
The Bannon Professional Services team actively embraces and adheres to the latest RICS Valuation Practice Guidance Note titled ‘Sustainability and ESG in Commercial Property Valuation and Strategic Advice’ when undertaking valuation instructions. This Guidance Note requires the valuer to demonstrate how they have considered sustainability and ESG credentials in their valuation approach, calculations and commentary. It may be necessary, depending on the nature of the instruction, for the valuer to seek specialist investigations by a third party advising as to the ability and estimated cost to bring an asset up to modern standards. Valuing assets of this nature requires an in-depth analysis of the true costs associated with bringing them up to standard.
Property Management from Director Ray Geraghty
 Sustainability is a key focus of the Bannon Property Management team. The extent of our portfolio (150 assets) gives Bannon a unique position in the Irish marketplace to be leaders of change. At present there are a variety of ongoing projects across the portfolio which are focused on reducing energy consumption, reducing water consumption and reducing waste.
Sustainability is a key focus of the Bannon Property Management team. The extent of our portfolio (150 assets) gives Bannon a unique position in the Irish marketplace to be leaders of change. At present there are a variety of ongoing projects across the portfolio which are focused on reducing energy consumption, reducing water consumption and reducing waste.
Office from Divisional Director Lucy Connolly
 Sustainability in terms of office design and construction has become a fundamental and determining factor for companies when acquiring office space. With corporate ESG agendas now firmly in place, what was once a consideration, is now a key component in the acquisition process, which in turn is leading to increased demand for prime grade A office accommodation.
Sustainability in terms of office design and construction has become a fundamental and determining factor for companies when acquiring office space. With corporate ESG agendas now firmly in place, what was once a consideration, is now a key component in the acquisition process, which in turn is leading to increased demand for prime grade A office accommodation.
Investment from Executive Director Rod Nowlan
 ESG has permeated every aspect of real estate, but in many ways has been led by the Capital Markets sector. Well before the adoption in April 2021 of EU’s Sustainable Finance Directive, major real estate players were readying themselves for the impact of ESG in terms of putting in place procedures for collating information and assessing and adjusting their assets and portfolios. These institutions have either been acquiring or developing compliant assets while simultaneously selling assets which would fall foul of ESG regulations. Most smaller fund managers and private offices have now followed suite. Now that ESG goes to the heart of any asset due diligence, non-complaint assets have a difficult future ahead of them! There will however be huge opportunity for those with the skills to efficiently transition these buildings back to the institutional mainstream. In this regard, valuing and selling these assets will require an in-depth analysis of the true costs associated with bringing them up to standard.
ESG has permeated every aspect of real estate, but in many ways has been led by the Capital Markets sector. Well before the adoption in April 2021 of EU’s Sustainable Finance Directive, major real estate players were readying themselves for the impact of ESG in terms of putting in place procedures for collating information and assessing and adjusting their assets and portfolios. These institutions have either been acquiring or developing compliant assets while simultaneously selling assets which would fall foul of ESG regulations. Most smaller fund managers and private offices have now followed suite. Now that ESG goes to the heart of any asset due diligence, non-complaint assets have a difficult future ahead of them! There will however be huge opportunity for those with the skills to efficiently transition these buildings back to the institutional mainstream. In this regard, valuing and selling these assets will require an in-depth analysis of the true costs associated with bringing them up to standard.

Why is the real estate sector being targeted to improve its environmental sustainability? The big numbers speak for themselves. It is the industry’s responsibility to improve these statistics. At Bannon we are proactively working to improve the environmental performance of Ireland’s Commercial Real Estate Sector.



Hambleden House
19-26 Pembroke Street Lower
Dublin 2
D02 WV96
Ireland
»Map
Phone: +353 (1) 6477900
Fax: +353 (1) 6477901
Email: info@bannon.ie


